Welding has been a cornerstone of manufacturing, construction, and repair for decades. From building skyscrapers to assembling medical devices, welding technology continues to evolve. Today, while traditional welding methods remain important, laser welding is rapidly gaining attention for its precision and efficiency.
In this blog, we’ll cover the 5 common types of welding and explain why laser welding is becoming more popular across industries.
1. Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
Also known as stick welding, SMAW is one of the oldest and most widely used welding techniques. It uses a consumable electrode coated in flux to create the weld.
-
Advantages: Low cost, portable, works well outdoors.
-
Limitations: Slower process, less precise, produces more slag.

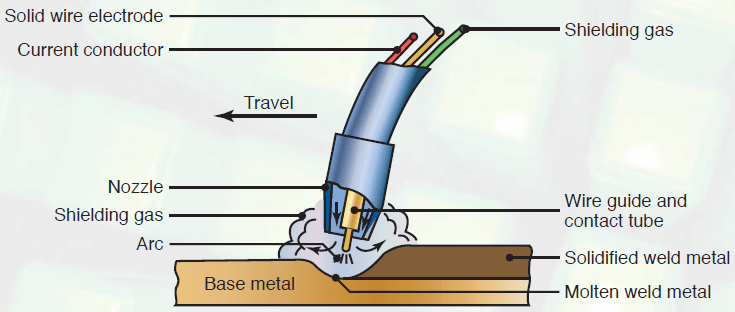
2. Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW/MIG)
MIG welding uses a wire electrode and shielding gas to create a clean weld. It’s often used in automotive, fabrication, and construction.
-
Advantages: Fast, easy to learn, produces cleaner welds than SMAW.
-
Limitations: Sensitive to wind and requires shielding gas supply.
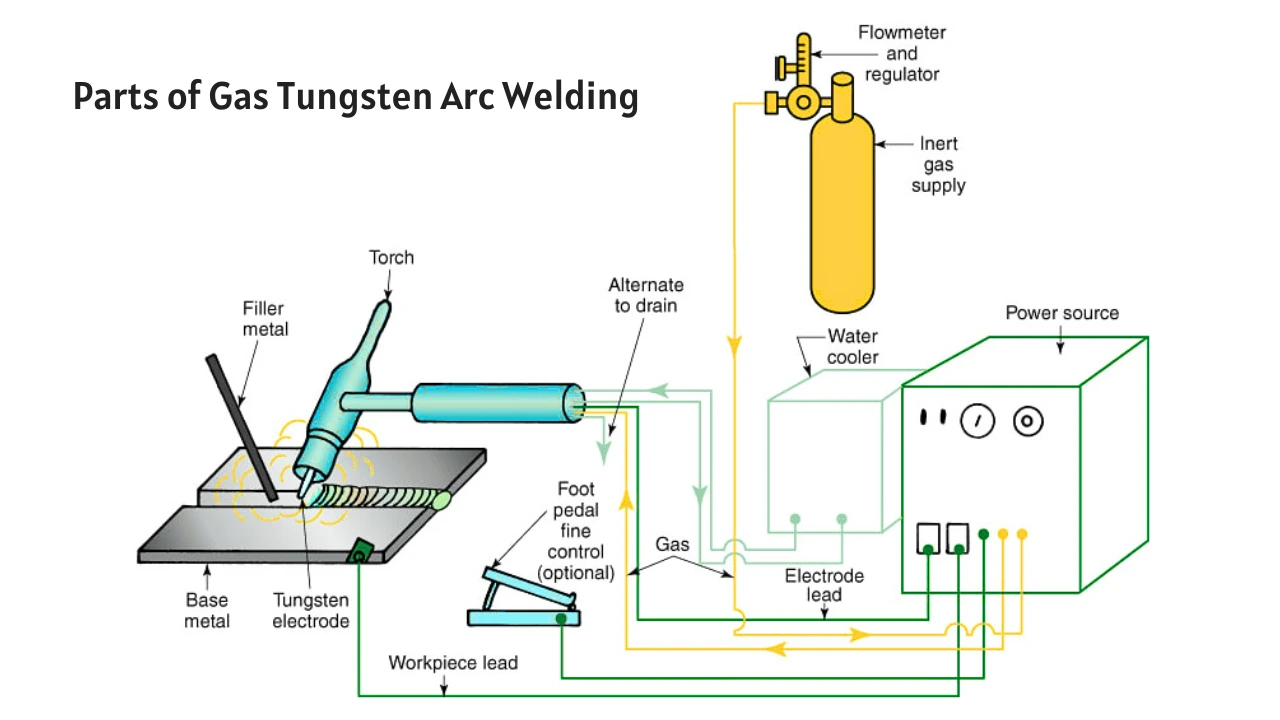
3. Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG)
TIG welding uses a tungsten electrode and inert gas, offering extremely precise and high-quality welds. It’s ideal for thin metals and aerospace applications.
-
Advantages: High precision, strong and clean welds, no spatter.
-
Limitations: Slower, requires more skill, higher cost.
4. Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
Similar to MIG welding, but uses a flux-filled wire instead of solid wire with shielding gas. Often used in heavy-duty construction and shipbuilding.
-
Advantages: Works outdoors, high deposition rates, good for thick materials.
-
Limitations: Produces more smoke and requires post-weld cleanup.

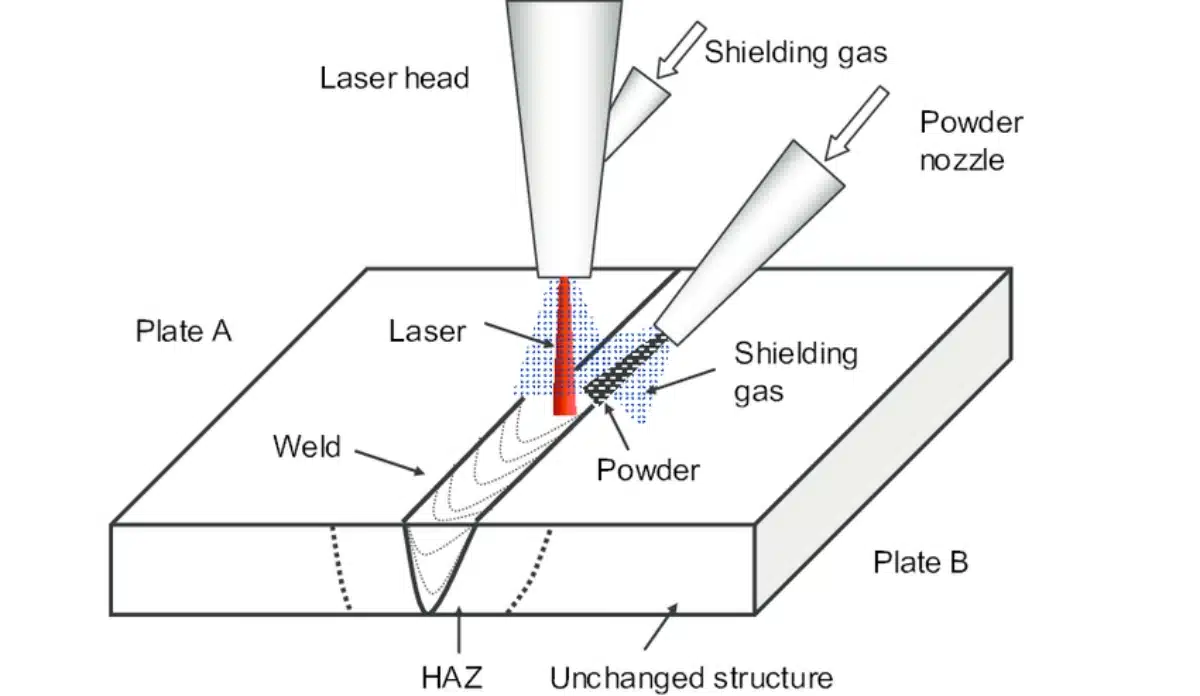
5. Laser Welding
Laser welding uses a high-powered laser beam to join metals or plastics. Unlike arc welding, it delivers heat in a narrow and precise area.
-
Advantages: Exact, minimal distortion, high-speed welding, suitable for automation.
-
Limitations: Higher equipment cost, requires safety measures for laser handling.
Why Is Laser Welding Becoming More Popular?
While traditional welding methods remain important, industries are shifting toward laser welding for several reasons:
-
Precision & Quality – Laser welding produces narrow, deep welds with minimal heat-affected zones, reducing distortion and improving product quality.
-
Speed & Efficiency – Automated laser welding can be 2–10 times faster than conventional methods, ideal for mass production.
-
Versatility – It works on metals, alloys, and even plastics, making it popular in electronics, medical devices, and automotive industries.
-
Automation-Ready – Laser welding integrates easily with CNC machines and robotic systems, supporting smart manufacturing.
-
Lower Long-Term Costs – Although the initial investment is higher, reduced labor costs, faster production, and fewer defects result in long-term savings.
Conclusion
Welding technology continues to evolve from traditional stick and MIG methods to advanced laser welding solutions. While each type of welding has its place, laser welding is quickly becoming the go-to method for industries demanding precision, efficiency, and scalability.
If your business requires fast, high-quality welds with minimal distortion, laser welding is the smarter choice for the future.
Post time: Sep-30-2025

